ALL WEATHER OPERATIONS
ALL WEATHER OPERATIONS
General requirements
All Weather Operations (AWO) means operating aircraft in Low Visibility Conditions (LVC). The term Low Visibility Operations (LVO) may be used in Company’s documents instead of AWO and includes:
CM1 and CM2 shall be qualified and current for LVTO and applicable LVO approach. Allocation of PF/PNF between CM1 and CM2 (CM1 is always PF) shall be strictly adhered to.
In an event of aeroplane and/or ground system malfunction occurring in LVC below 1000 ft. AGL which requires corrective action and/or procedure modification a go-around must be executed.
Aeroplane specific operating procedures (as defined in OM Part B) shall be strictly adhered to. CAT II/III instrument approach and landing operations are not authorised unless RVR information is provided.
Where decision height (DH) and runway visual range (RVR) fall into different categories of operation, the instrument approach and landing operation would be conducted in accordance with the requirements of the most demanding category (e.g. an operation with a DH in the range of CAT II but with an RVR in the range of CAT I would be considered a CAT II operation).
The Company shall not conduct Category II/III operations unless:
LVTO is a take-off where the RVR is less than 400 m.
When weather condition on departure aerodrome is below the landing minima, a take-off alternate should be nominated equal to or better than CAT I minima and noted on OFP. This take-off alternate should be within one hour of flight with one-engine inoperative (330 NM). Terrain and weather en-route to take-off alternate must permit single-engine operation.
When the reported meteorological visibility is below that required for take-off and RVR is not reported, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum.
When no reported meteorological visibility or RVR is available, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum.
When no reported meteorological visibility or RVR is available, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum. CM1 is PF.
For LVTO, aeroplane configuration and performance calculations resulting in lowest safe take-off speeds should be considered even on the expense of increased required take-off thrust.
The Company shall not conduct LVTO in less than 150m RVR (CAT C aircraft) unless approved by the Authority.
Rejected Take-off during LVTO:
(ICAO): A Category II operation (CAT II) is a precision instrument approach and landing using ILS with:
Required Visual Reference
Must contain a segment of at least 3 consecutive lights being the:
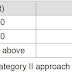
The lowest minima to be used for Category II operations (aircraft category C) are:
Precision Category III Approach (CAT III / CAT 3)
A Category III operation (CAT III) is a precision instrument approach and landing using ILS, further divided into
CAT IIIA (CAT 3A):
• RVR of not less than 200 m, and
• Decision Height below 100 ft and not lower than 50 ft.
CAT IIIB (CAT 3B):
• RVR less than 200 m but not less than 75 m (125 m being Company limitation!), and
• Decision Height below 50 ft or NO Decision Height.
On a CAT 3 runway, it may be assumed that operations with NO Decision Height can be supported, unless specifically restricted, as published in the AIP or NOTAM.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIA Approach
Must contain a segment of at least 3 consecutive lights being:
• The centre line of the approach lights, or
• Touchdown zone lights, or
• Runway centre line lights, or
• Runway edge lights, or
• A combination of these.
The visual references once attained must be maintained.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIB Approach with a Decision Height
Must contain a segment at least one centre line light and once attained must be maintained.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIB Approach with NO Decision Height
There is no requirement for visual reference to be established prior to touchdown.
Definitions
Low Visibility Operations (LVO): Means operating aircraft (taxi, take-off or landing) in Low Visibility Conditions (LVC). LVO operations include Low Visibility Taxi, Take-Off and CAT II/III approaches in LVC.
Low Visibility Procedures (LVP): Procedures applied at an aerodrome for the purpose of ensuring safe operations during ILS CAT II and ILS CAT III approaches and low visibility take-offs.
Low Visibility Conditions (LVC): LVC for take-off and landing are defined below:
Low Visibility Take-off (LVTO): A take-off where runway visual range (RVR) is less than 400 m.
Decision Height (DH): Decision height is a wheel height above runway elevation by which a go-around must be initiated unless adequate visual reference has been established and aeroplane position and approach path have been assessed as satisfactory to continue approach and landing in safety. In this definition, runway elevation means elevation of the highest point in touchdown zone. DH recognition must be, by means of height, measured by the radio altimeter.
Decision Height Concept: Decision Height is the specified point in space at which a pilot must make an operational decision. A pilot must decide if visual references, adequate to safely continue the approach, have been established. If visual references have not been established, a go-around must be executed. If required visual references have been established, an approach can be continued. Nevertheless, a Commander may always decide to execute a go-around if sudden degradations in visual references or sudden flight path deviation occur. When necessary, published DH takes into account terrain profile before runway threshold.
Decision Altitude (DA): A specified altitude in approach at which missed approach must be initiated if required visual reference to continue has not been established. Decision Altitude (DA) is referenced to Mean Sea Level (MSL).
Alert Height (ICAO): Alert Height is height above the runway, based on characteristics of an aeroplane and its fail-operational automatic landing system, above which CAT 3 approach would be discontinued and missed approach initiated if a failure occurred in one of the redundant parts of automatic landing system, or in relevant ground equipment. In other AH definitions it is generally stated that if a failure occurred below Alert Height, it would be ignored and approach continued.
Alert Height Concept - Alert Height (AH) is height defined for ILS CAT 3 operations with fail-operational landing system. Above AH, a go-around must be initiated if failure affects fail-operational landing system. Below AH, an approach may be continued except if a specific warning is triggered. AH is evaluated during aeroplane certification. In general, more sophisticated fail-operational landing systems will determine higher AH.
Fail-Passive Flight Control System: A flight control system is Fail-Passive if, in an event of a failure, there is no significant out-of-trim condition or deviation of flight path or attitude but landing is not completed automatically. For Fail-Passive Automatic Flight Control System, a pilot assumes control of the aeroplane after a failure.
Fail-Operational Flight Control System: A Flight Control System is Fail-Operational if, in event of a failure below alert height, approach, flare and landing can be completed automatically. In event of a failure, automatic landing system will operate as the fail-passive system.
Runway Visual Range (RVR): A range of which a Commander of an aircraft on a centerline of a runway can see runway surface markings or lights delineating runway or identifying its centreline.
Converted Meteorological Visibility (CMV): A value (equivalent to RVR) which is derived from reported meteorological visibility.
Minimum Approach Break-Off Height (MABH): Is the lowest height above the ground, measured by radio altimeter, such that if a missed approach is initiated without external references:
•In normal operation, the aircraft does not touch the ground during the procedure.
•With an engine failure during a missed approach, it can be demonstrated that taking this failure probability, an accident is extremely improbable.
General requirements
All Weather Operations (AWO) means operating aircraft in Low Visibility Conditions (LVC). The term Low Visibility Operations (LVO) may be used in Company’s documents instead of AWO and includes:
- Low Visibility Taxi,
- Low Visibility Take-Off (LVTO),
- Precision Approach ILS Category II (Cat 2 / Cat II),
- Precision Approach ILS Category III (Cat 3 / Cat III).
- The status of the visual and non-visual facilities is sufficient;
- Appropriate LVPs are in force according to information received from ATS;
- The flight crew members are properly qualified.
CM1 and CM2 shall be qualified and current for LVTO and applicable LVO approach. Allocation of PF/PNF between CM1 and CM2 (CM1 is always PF) shall be strictly adhered to.
In an event of aeroplane and/or ground system malfunction occurring in LVC below 1000 ft. AGL which requires corrective action and/or procedure modification a go-around must be executed.
Aeroplane specific operating procedures (as defined in OM Part B) shall be strictly adhered to. CAT II/III instrument approach and landing operations are not authorised unless RVR information is provided.
Where decision height (DH) and runway visual range (RVR) fall into different categories of operation, the instrument approach and landing operation would be conducted in accordance with the requirements of the most demanding category (e.g. an operation with a DH in the range of CAT II but with an RVR in the range of CAT I would be considered a CAT II operation).
The Company shall not conduct Category II/III operations unless:
- Each aeroplane concerned is certificated for operations with decision heights below 200ft, or no decision height, and equipped in accordance with the aircraft certification for all weather operations or an equivalent accepted by the SSCA,
- A suitable system for recording approach and/or automatic landing success and failure is established and maintained to monitor the overall safety of the operation,
- The operations are approved by the SSCA,
- The flight crew consists of at least two pilots,
- Decision height is determined by means of a radio altimeter,
- Only RVR values are used for low visibility operations.
LVTO is a take-off where the RVR is less than 400 m.
When weather condition on departure aerodrome is below the landing minima, a take-off alternate should be nominated equal to or better than CAT I minima and noted on OFP. This take-off alternate should be within one hour of flight with one-engine inoperative (330 NM). Terrain and weather en-route to take-off alternate must permit single-engine operation.
When the reported meteorological visibility is below that required for take-off and RVR is not reported, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum.
When no reported meteorological visibility or RVR is available, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum.
When no reported meteorological visibility or RVR is available, a take-off may only be commenced if the commander can determine that the RVR/visibility along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum. CM1 is PF.
For LVTO, aeroplane configuration and performance calculations resulting in lowest safe take-off speeds should be considered even on the expense of increased required take-off thrust.
The Company shall not conduct LVTO in less than 150m RVR (CAT C aircraft) unless approved by the Authority.
Rejected Take-off during LVTO:
- If visual references are lost below 100 kits, take-off should be rejected.
- If visual references are lost above 100 kits, take-off should be continued utilising approved lateral guidance system (e.g. yaw bar).
- If take-off was rejected, the CM1 should switch all landing lights ON so that emergency services can easily identify aeroplane in low visibility conditions.
(ICAO): A Category II operation (CAT II) is a precision instrument approach and landing using ILS with:
- RVR of not less than 350 m, and
- Decision Height below 200 ft and not lower than 100 ft.
- Minimum DH specified in the AFM,
- Minimum height to which the precision approach aid can be used without the required visual reference,
- OCH/OCL for the category of the aircraft,
- DH to which the flight crew is authorised to operate,
- 100 ft.
Required Visual Reference
Must contain a segment of at least 3 consecutive lights being the:
- The centre-line of the approach lights (CL of the APL) or,
- Touchdown zone lights (TDZL), or Runway centre line lights (RCLL), or
- Runway edge lights (REDL), or
- A combination of these.
The lowest minima to be used for Category II operations (aircraft category C) are:
Precision Category III Approach (CAT III / CAT 3)
A Category III operation (CAT III) is a precision instrument approach and landing using ILS, further divided into
CAT IIIA (CAT 3A):
• RVR of not less than 200 m, and
• Decision Height below 100 ft and not lower than 50 ft.
CAT IIIB (CAT 3B):
• RVR less than 200 m but not less than 75 m (125 m being Company limitation!), and
• Decision Height below 50 ft or NO Decision Height.
On a CAT 3 runway, it may be assumed that operations with NO Decision Height can be supported, unless specifically restricted, as published in the AIP or NOTAM.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIA Approach
Must contain a segment of at least 3 consecutive lights being:
• The centre line of the approach lights, or
• Touchdown zone lights, or
• Runway centre line lights, or
• Runway edge lights, or
• A combination of these.
The visual references once attained must be maintained.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIB Approach with a Decision Height
Must contain a segment at least one centre line light and once attained must be maintained.
Required Visual Reference, Category IIIB Approach with NO Decision Height
There is no requirement for visual reference to be established prior to touchdown.
Definitions
Low Visibility Operations (LVO): Means operating aircraft (taxi, take-off or landing) in Low Visibility Conditions (LVC). LVO operations include Low Visibility Taxi, Take-Off and CAT II/III approaches in LVC.
Low Visibility Procedures (LVP): Procedures applied at an aerodrome for the purpose of ensuring safe operations during ILS CAT II and ILS CAT III approaches and low visibility take-offs.
Low Visibility Conditions (LVC): LVC for take-off and landing are defined below:
Low Visibility Take-off (LVTO): A take-off where runway visual range (RVR) is less than 400 m.
Decision Height (DH): Decision height is a wheel height above runway elevation by which a go-around must be initiated unless adequate visual reference has been established and aeroplane position and approach path have been assessed as satisfactory to continue approach and landing in safety. In this definition, runway elevation means elevation of the highest point in touchdown zone. DH recognition must be, by means of height, measured by the radio altimeter.
Decision Height Concept: Decision Height is the specified point in space at which a pilot must make an operational decision. A pilot must decide if visual references, adequate to safely continue the approach, have been established. If visual references have not been established, a go-around must be executed. If required visual references have been established, an approach can be continued. Nevertheless, a Commander may always decide to execute a go-around if sudden degradations in visual references or sudden flight path deviation occur. When necessary, published DH takes into account terrain profile before runway threshold.
Decision Altitude (DA): A specified altitude in approach at which missed approach must be initiated if required visual reference to continue has not been established. Decision Altitude (DA) is referenced to Mean Sea Level (MSL).
Alert Height (ICAO): Alert Height is height above the runway, based on characteristics of an aeroplane and its fail-operational automatic landing system, above which CAT 3 approach would be discontinued and missed approach initiated if a failure occurred in one of the redundant parts of automatic landing system, or in relevant ground equipment. In other AH definitions it is generally stated that if a failure occurred below Alert Height, it would be ignored and approach continued.
Alert Height Concept - Alert Height (AH) is height defined for ILS CAT 3 operations with fail-operational landing system. Above AH, a go-around must be initiated if failure affects fail-operational landing system. Below AH, an approach may be continued except if a specific warning is triggered. AH is evaluated during aeroplane certification. In general, more sophisticated fail-operational landing systems will determine higher AH.
Fail-Passive Flight Control System: A flight control system is Fail-Passive if, in an event of a failure, there is no significant out-of-trim condition or deviation of flight path or attitude but landing is not completed automatically. For Fail-Passive Automatic Flight Control System, a pilot assumes control of the aeroplane after a failure.
Fail-Operational Flight Control System: A Flight Control System is Fail-Operational if, in event of a failure below alert height, approach, flare and landing can be completed automatically. In event of a failure, automatic landing system will operate as the fail-passive system.
Runway Visual Range (RVR): A range of which a Commander of an aircraft on a centerline of a runway can see runway surface markings or lights delineating runway or identifying its centreline.
Converted Meteorological Visibility (CMV): A value (equivalent to RVR) which is derived from reported meteorological visibility.
Minimum Approach Break-Off Height (MABH): Is the lowest height above the ground, measured by radio altimeter, such that if a missed approach is initiated without external references:
•In normal operation, the aircraft does not touch the ground during the procedure.
•With an engine failure during a missed approach, it can be demonstrated that taking this failure probability, an accident is extremely improbable.
ALL WEATHER OPERATIONS
 Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:12 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:12 PM
Rating:
 Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:12 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:12 PM
Rating:






No comments: