METHODS FOR ESTABLISHING AERODROME OPERATING MINIMA
Aerodrome Operating Minima – General
The term Aerodrome Operating Minima refers to the minimum weather conditions required for particular operations at an aerodrome and are expressed in terms of cloud ceiling, RVR and visibility.
Required minima are affected by:
Aerodrome Operating Minima defines the limits of usability of an aerodrome for either take-off or landing, usually expressed in terms of RVR or VIS, DA (H), MDA (H) and cloud conditions. Unless stated otherwise AOM are depicted on aeronautical charts (refer to OM Part C) and never below any State minima.
Aeroplane capability given in the OM Part B defines the lowest minima for which an aeroplane has been certified.
The Company Minima are approved by the Authority and stated in the AOC Operational Specifications. They are the lowest minima that The Company is allowed to use on specified aerodromes. They cannot be lower than the aeroplane capability and the minima required by the national Authority of the aerodrome.
Crew minima are the minima to which individual flight crew members are authorised to use. They are based upon the training and qualification of the flight crew members.
Aeroplane Approach Categories
For approach, aeroplanes are classified in categories A, B, C, D, and E.
A320 aircraft, operated by The Company, are classified as Category C aeroplanes (refer to OM Part B). The criteria taken into consideration for the classification of aeroplanes by categories is the IAS at threshold (VAT) in landing configuration at the maximum certified landing weight.
Aircraft Category VAT
C 121 - 140 knots
The category is a permanent value and is independent of the changing conditions of day to day operations.
Take-off Operating Minima
Take-off minima are generally expressed as VIS or RVR Limits. Where there is a specific need to see and avoid obstacles, a ceiling or climb gradient will be specified.
Important: The Company is currently not approved to conduct LVTO.
Authorized Approaches
The approach procedures published in the OM Part C for ILS, PAR, LOC (GS inoperative), VOR, VOR/DME, SRA, NDB and NDB/DME are authorized, provided:
A visual approach takes place when either part or all of an instrument approach procedure is not completed and approach is executed by visual reference to the terrain. Visual approach shall not be attempted unless:
Circling is the term used to describe the visual phase of an instrument approach required to position an aeroplane for landing on a runway, which is not suitably located for a straight-in approach. During circling manoeuvres the relevant approach category is associated with a maximum speed for manoeuvring. In the case of category C this speed is normally 180 kt. Circle-to-land approach shall not be attempted unless:
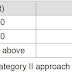
MDH 600 ft
VIS 2400 m
Circle-to-land Minima
The term Aerodrome Operating Minima refers to the minimum weather conditions required for particular operations at an aerodrome and are expressed in terms of cloud ceiling, RVR and visibility.
Required minima are affected by:
- Aircraft Capability – defined in the Airplane Flight Manual (AFM) and described in OM part B and FCOM;
- Obstacle Clearance and Procedure Type – calculated in accordance with ICAO Document 8168;
- Operator’s Approved Minima;
- Crew Minima;
- Aircraft system degradation;
- Ground system degradation;
- Aeroplane category.
Aerodrome Operating Minima defines the limits of usability of an aerodrome for either take-off or landing, usually expressed in terms of RVR or VIS, DA (H), MDA (H) and cloud conditions. Unless stated otherwise AOM are depicted on aeronautical charts (refer to OM Part C) and never below any State minima.
Aeroplane capability given in the OM Part B defines the lowest minima for which an aeroplane has been certified.
The Company Minima are approved by the Authority and stated in the AOC Operational Specifications. They are the lowest minima that The Company is allowed to use on specified aerodromes. They cannot be lower than the aeroplane capability and the minima required by the national Authority of the aerodrome.
Crew minima are the minima to which individual flight crew members are authorised to use. They are based upon the training and qualification of the flight crew members.
Aeroplane Approach Categories
For approach, aeroplanes are classified in categories A, B, C, D, and E.
A320 aircraft, operated by The Company, are classified as Category C aeroplanes (refer to OM Part B). The criteria taken into consideration for the classification of aeroplanes by categories is the IAS at threshold (VAT) in landing configuration at the maximum certified landing weight.
Aircraft Category VAT
C 121 - 140 knots
The category is a permanent value and is independent of the changing conditions of day to day operations.
Take-off Operating Minima
Take-off minima are generally expressed as VIS or RVR Limits. Where there is a specific need to see and avoid obstacles, a ceiling or climb gradient will be specified.
- Take-off shall not be commenced unless weather conditions at the airport of departure are equal to or better than applicable minima for landing at that airport, unless a suitable takeoff alternate aerodrome is available is available within 330 NM for jet aeroplanes.
- When the reported visibility VIS is below that required for take-off and RVR is not reported, a take-off may only be commenced if the Commander can determine that the RVR along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minimum.
- When no report of VIS or RVR is available, a take-off may only be commenced if the Commander can determine that the RVR along the take-off runway is equal to or better than the required minima.
Important: The Company is currently not approved to conduct LVTO.
Authorized Approaches
The approach procedures published in the OM Part C for ILS, PAR, LOC (GS inoperative), VOR, VOR/DME, SRA, NDB and NDB/DME are authorized, provided:
- All the required navigation aids, as specified in the title of the approach charts are available during the appropriate phases of an approach;
- The minimum required equipment on board, to use the specified navigation aids is serviceable.
A visual approach takes place when either part or all of an instrument approach procedure is not completed and approach is executed by visual reference to the terrain. Visual approach shall not be attempted unless:
- ATC clearance for visual approach has been issued;
- It is daytime;
- Reported cloud ceiling is higher than MDH specified in approach chart (under circle to-land) or 1500 ft, whichever is greater;
- Reported visibility is at least 5000 m;
- Reported RVR on applicable parts of landing runway is at least 800 m.
- Visual approach shall not be initiated and/or continued unless:
- The aeroplane is clear of clouds;
- The active runway and/or runway lights and/or approach lights and/or other lights, markings or objects identifiable with the runway can be kept in sight.
Circling is the term used to describe the visual phase of an instrument approach required to position an aeroplane for landing on a runway, which is not suitably located for a straight-in approach. During circling manoeuvres the relevant approach category is associated with a maximum speed for manoeuvring. In the case of category C this speed is normally 180 kt. Circle-to-land approach shall not be attempted unless:
- ATC clearance for circle-to-land has been issued;
- Reported cloud ceiling is equal or higher than MDH specified in approach chart (under circle-to-land) or MDH specified in table Circle-to-land Minima below, whichever is greater;
- Reported visibility is equal or greater than minimum required specified in approach chart (under circle-to-land) or visibility specified in table Circle-to-land Minima below, whichever is greater;
- Reported RVR on applicable parts of landing runway is at least 800 m.
- The aeroplane is clear of clouds;
- The active runway and/or runway lights and/or approach lights and/or other lights, markings or objects identifiable with the runway can be kept in sight.
MDH 600 ft
VIS 2400 m
Circle-to-land Minima
METHODS FOR ESTABLISHING AERODROME OPERATING MINIMA
 Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:43 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:43 AM
Rating:
 Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:43 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Aviation Lesson
on
9:43 AM
Rating:





No comments: